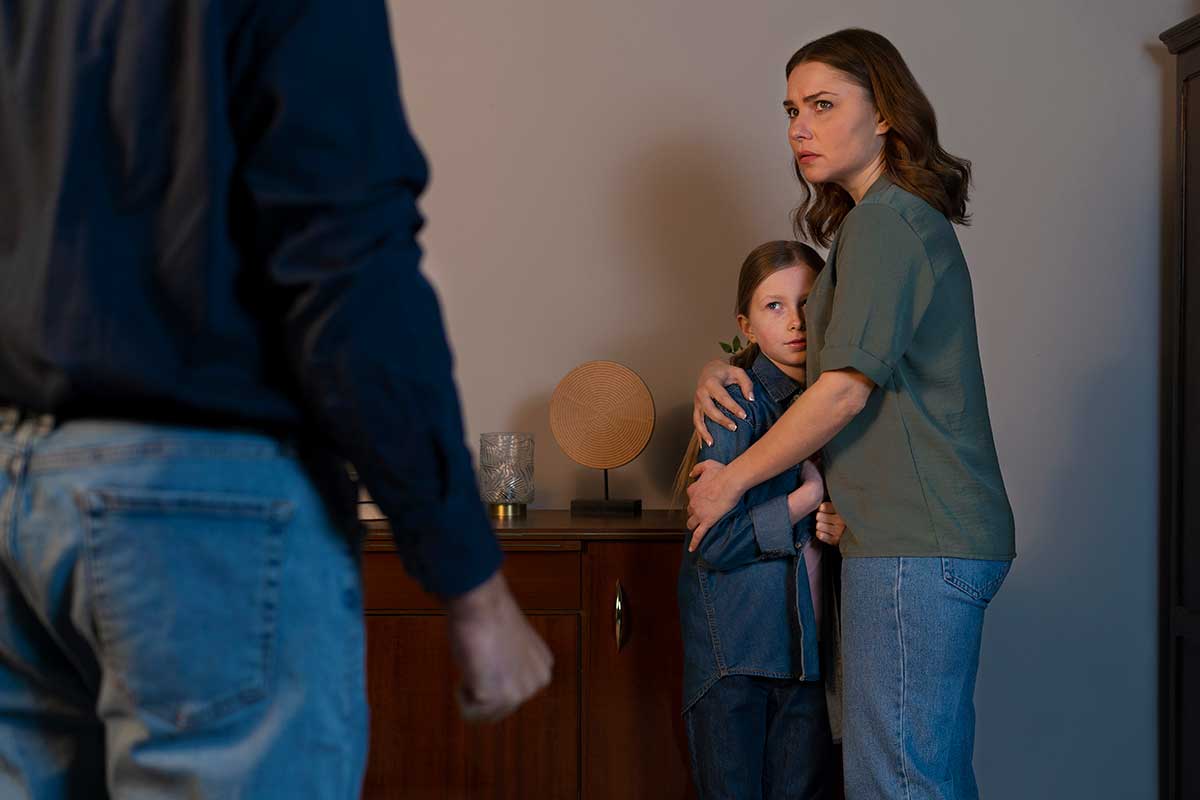The United States faces a staggering number of individuals grappling with substance abuse, a pressing issue that permeates our society. A sobering report by the United States Surgeon General in 2017 revealed that an American adult dies of heroin or opioid overdose every 19 minutes, resulting in an alarming loss of life.
Beyond the devastating toll on individuals, the economic impact of drug addiction stands at a staggering $442 billion annually. However, the repercussions extend well beyond those who directly suffer from substance abuse, impacting their families and communities in equally profound and distressing ways.
DeCoach Rehabilitation Centre offers a private setting where clients can undergo withdrawal with utmost privacy, prioritizing their safety and well-being. Our dedicated interdisciplinary team ensures the highest quality of medical care during the withdrawal management (WM) phase, facilitating a secure transition to the subsequent aftercare stage.
In this article, we’ll discuss how SUDs affect families and the broader community.
How Does a Substance Use Disorder Affect a Family?
Impact on Young Children
It is estimated that 1 in 5 American children grows up in a household where a parent abuses drugs or alcohol. Bearing witness to a parent’s battle with addiction during their formative years has enduring effects on these children. They are more prone to developing Substance Use Disorders (SUDs) in adulthood, with a threefold increased likelihood of experiencing neglect or physical and/or sexual abuse. The distressing spectacle of a parent under the influence of drugs not only hampers learning and development but also predisposes children to long-lasting mental and emotional disorders.
Given their vulnerable state and ongoing personality development, children run the risk of perpetuating these detrimental behaviors. They may be exposed to aggression or violent behavior resulting from a parent’s alcohol consumption. Witnessing familial disputes becomes an unfortunate norm, inflicting emotional anguish upon the child as they bear witness to their loved ones’ downward spiral.
Early exposure to a household divided by drug use leaves children emotionally and physically neglected, and a sense of insecurity pervades their lives. Consequently, they are susceptible to heightened mental and emotional instability.
Feelings of extreme guilt and self-blame may manifest in response to a parent’s substance abuse, leading to a sense of unworthiness or dysfunctional attachments in their adult lives. In severe cases, children may be forcibly removed from their homes and placed in foster care.
The Impact of Teenage Addiction on the Family
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) report that underage drinkers consume more alcoholic beverages per occasion than their adult counterparts. Approximately 20.9% of teens aged 14 to 15 report having at least one drink in their lifetime. Moreover, marijuana use is more prevalent among teenagers than cigarette smoking. Adolescents grapple with the pressures of peer influence in educational settings while being persistently confronted by temptations.
As teenagers forge their identities, they remain impressionable, and a parental history of substance abuse further heightens their vulnerability to substance misuse in adulthood. Teenage addiction stems from a combination of external factors, such as peer pressure, and internal factors, such as genetic predispositions.
Stimulants like cocaine disrupt teenagers’ sleep patterns, leading to impaired academic performance. Meanwhile, opioids yield temporary euphoria but exact a heavy toll through frequent usage and subsequent damaging side effects.
The Family as Collateral Damage
When a single family member succumbs to addiction, the entire family unit bears the brunt of the consequences. The ripple effects manifest in various ways, including:
- Physical and emotional side effects
- Withdrawal symptoms
- Strained relationships
- Financial hardships
- Poor academic performance
- Exposure to other drugs
- Reckless behavior within the home
- Theft to sustain addictive habits
- Escaping from home
- Causing parental distress
Overwhelmed by addictive substances and strained familial dynamics, teenagers may contemplate running away from home. Parental distress can inadvertently push troubled adolescents toward substances as an escape, leaving them vulnerable to sexual, economic, and emotional exploitation.
The Social Impact of Substance Use Disorders
Substance Use Disorders (SUDs) profoundly impact individuals’ social functioning, creating a burden that extends beyond the individual to society. These disorders contribute to medical and psychiatric conditions, disabilities, and even fatalities resulting from accidents or diseases caused or worsened by substance use. Furthermore, they are linked to higher rates of suicidality, housing instability, homelessness, involvement in criminal behaviors as victims or perpetrators, the transmission of HIV due to intravenous drug use or risky sexual behaviors, and unemployment or dependence on welfare.
The social problems associated with SUDs impose an overwhelming economic burden on governments who allocate significant resources to addiction treatment, medical and psychiatric interventions, and addressing related issues like welfare dependence, unemployment, and involvement in the criminal justice and social service systems.
Interventions Addressing Social and Family Problems
Comprehensive treatment for SUDs encompasses a range of professional addiction and related services, including assessment, detoxification, rehabilitation, counseling or therapy, continuing care, substance use monitoring, medications, case management, and mutual support programs.
Addressing social, family, and other challenges requires utilizing various services available within addiction treatment agencies or the community at large, such as family, child care, vocational, mental health, medical, educational, HIV/AIDS, legal, financial, housing, and transportation services.
Both individual and group treatments for SUDs have been developed to address social recovery issues, recognizing their impact on relapse and overall quality of life. These interventions focus on essential aspects such as avoiding or minimizing contact with high-risk individuals or environments, resolving relationship problems, cultivating new friendships, building a network of supportive and sober individuals, resisting social pressures to use substances, enhancing communication and assertiveness skills, seeking help and support from others.
Family interventions play a crucial role in motivating and supporting individuals with SUDs to seek treatment, addressing the impact of the SUD on the family system and its members, and enabling families to manage their own reactions and associated problems. Active participation in treatment and family support programs can facilitate the healing process.
Considerable literature supports the efficacy of couples and family approaches to SUDs. These approaches alleviate the emotional burden experienced by family members, enabling them to cope more effectively with the challenges posed by their loved one’s SUD.
Here are some strategies that are used to assist families:
- Engaging the family in care:
- Involving the family in the assessment process and early stages of treatment.
- Employing outreach efforts to engage families in treatment.
- Providing education to families
- Offering information on SUDs, including symptoms, causes, and effects.
- Educating families about available treatments, including medication-assisted options.
- Addressing recovery challenges faced by individuals with SUDs.
- Educating families about relapse, mutual support programs, and the impact of SUDs on families and individuals.
- Informing families about professional services and mutual support programs available to them
- Offering or facilitating family treatment
- Conducting couples or family sessions to address questions, concerns, and interactions within the family system.
- Fostering improved communication and behavioral changes within the family.
- Providing a supportive environment through individual family sessions or multiple family groups, enabling shared experiences and learning from one another.
- Reducing the emotional burden on the family
- Recognizing and addressing the wide range of emotions experienced by family members, such as anger, fear, anxiety, and depression.
- Providing support and assistance to families.
- Encouraging connections with other families facing similar challenges.
- Facilitating opportunities for families to express their feelings and concerns and empowering them with information and coping skills. As families become more knowledgeable and equipped to navigate the complexities of addiction, their emotional burden tends to lessen.
5.Assisting the family in supporting the individual with the SUD
- Conducting joint sessions to help family members understand how they can support their loved one without enabling destructive behaviors.
- Educating family members about recognizing warning signs of relapse and intervening early in the process.
- Involving family members in discussions about a continuing care plan following completion of a rehabilitation program.
By engaging families in care, providing education, facilitating family treatment, reducing emotional burdens, and empowering families to support their loved ones, interventions can effectively address the social and family problems associated with SUDs.
It is essential to recognize that addressing substance abuse and its impact on families and communities requires a comprehensive and multifaceted approach. Collaboration between addiction treatment services, social support systems, healthcare providers, and community resources is crucial to provide holistic care and support to individuals and their families affected by substance abuse. By addressing these issues, we can strive towards mitigating the devastating consequences of addiction and fostering healthier, more resilient communities.
Mental Health & Addiction Treatment Services Available in Cincinnati, Fairfield, Hamilton, Xenia, and Fairborn Ohio
DeCoach Rehabilitation Centre offers cost-effective, expert, and secure Medication-Assisted Treatment for individuals seeking recovery from alcohol and opiate addiction. Our dedicated team of professionals takes a personalized approach to each patient’s treatment journey, providing individualized counseling within a serene and respectful setting.
If you or a loved one have questions regarding medication-assisted treatment or want to start the recovery journey, don’t hesitate to contact the compassionate team at DeCoach Rehabilitation Centre for further guidance and information.
To connect with one of our team members, call our offices or reach out to us online today!